Can Fibroids Cause Infertility or Delay Pregnancy?
Fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus. Many women have fibroids at some point in their lives, often without even knowing it. While fibroids are common, a frequent concern among women trying to conceive is: Can fibroids cause infertility or delay pregnancy?
The simple answer is — yes, fibroids can sometimes affect fertility, but not in every case. Many women with fibroids get pregnant naturally and deliver healthy babies. The effect of fibroids on fertility mainly depends on their size, number, and location inside the uterus.
This blog explains everything in simple language — how fibroids affect fertility, when they cause problems, available treatments, and what to do if you are planning a pregnancy.
Understanding Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are benign (non-cancerous) tumors made of muscle and tissue that grow in the uterus. They can be as small as a seed or as large as a melon. Some women have a single fibroid, while others may have multiple fibroids.
Fibroids usually grow during reproductive years and may shrink after menopause. At a specialized Fertility Clinic in Kenya, doctors often evaluate fibroids as part of routine fertility assessment to understand whether they are impacting pregnancy chances.
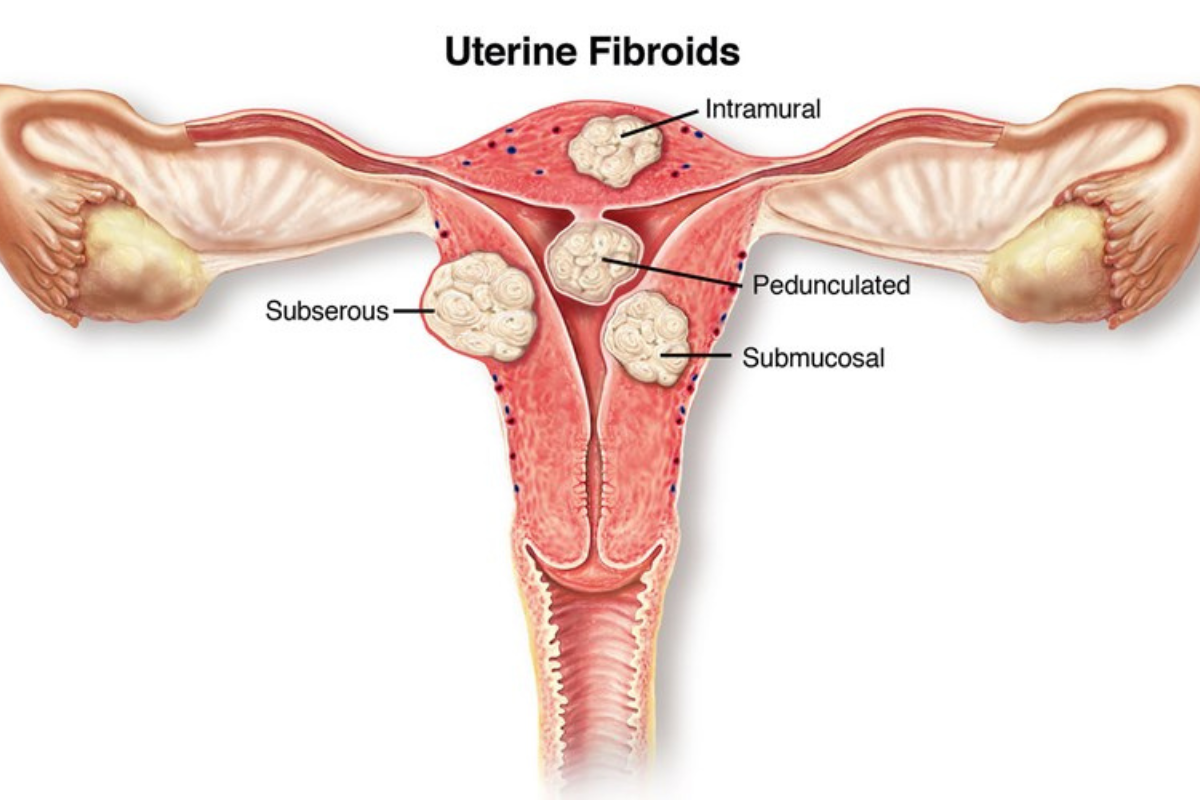
Types of Fibroids
Fibroids are classified based on where they grow in relation to the uterus. Understanding the type of fibroid is important because each type can affect symptoms, fertility, and pregnancy in different ways. Some fibroids cause no problems at all, while others may interfere with conception or cause discomfort.
Below are the main types of fibroids explained in simple language.
1. Submucosal Fibroids
Submucosal fibroids grow just beneath the inner lining of the uterus and extend into the uterine cavity. These fibroids are less common but are considered the most likely to affect fertility and pregnancy because they directly disturb the space where implantation occurs.
They can change the shape of the uterine cavity, making it harder for an embryo to attach properly or grow normally.
Key points about submucosal fibroids:
- Grow inside the uterine cavity
- Most strongly linked to infertility
- Can interfere with embryo implantation
- May increase the risk of miscarriage
- Often recommended for treatment when pregnancy is planned
2. Intramural Fibroids
Intramural fibroids develop within the muscular wall of the uterus. They are the most common type of fibroid and may or may not affect fertility depending on their size and position.
Smaller intramural fibroids often cause no fertility issues, but larger ones can distort the uterine shape or reduce blood flow to the uterine lining.
Key points about intramural fibroids:
- Located within the uterine muscle
- May affect fertility if large
- Can distort the uterine cavity when they grow
- May cause heavy periods and pelvic pain
- Fertility impact depends on size and location
3. Subserosal Fibroids
Subserosal fibroids grow on the outer surface of the uterus. These fibroids usually do not interfere with fertility, as they do not affect the uterine cavity, where implantation occurs.
However, if they become very large, they may cause pressure symptoms by pressing on nearby organs.
Key points about subserosal fibroids:
- Grow outside the uterus
- Least likely to affect fertility
- Usually, do not interfere with implantation
- Can cause pelvic pressure or back pain if large
- Often monitored without treatment
Can Fibroids Cause Infertility?
Yes, fibroids can cause infertility in some women, but they are not the most common cause. Fibroids are responsible for infertility in only a small percentage of cases.
Fibroids may affect fertility by:
- Blocking the fallopian tubes
- Distorting the uterine cavity
- Preventing embryo implantation
- Reducing the blood supply to the uterine lining
In many women, ovulation remains normal, but implantation becomes difficult.
How Fibroids affect the Ability to Get Pregnant
Fibroids can interfere with pregnancy in several ways:
1. Implantation Problems
Fibroids can alter the uterine lining, making it harder for an embryo to attach.
2. Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Fibroids near the tube openings may block the path of sperm or eggs.
3. Abnormal Uterine Contractions
Fibroids can disturb normal uterine movement, affecting embryo positioning.
4. Increased Risk of Miscarriage
Certain fibroids increase the risk of early pregnancy loss.
Symptoms of Fibroids That May Affect Fertility
Some fibroids cause no symptoms, but common warning signs include:
-
Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Severe menstrual pain
- Pelvic pressure or discomfort
- Frequent urination
- Pain during intercourse
- Difficulty conceiving
Women experiencing these symptoms while trying to conceive should seek evaluation.
How Fibroids are Diagnosed During Fertility Evaluation
Doctors may recommend:
- Pelvic ultrasound
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- Saline sonography
- Hysteroscopy
- MRI in selected cases
These tests help determine whether fibroids are affecting fertility.
Do All Fibroids Need Treatment Before Pregnancy?
No. Many fibroids do not require treatment. Treatment is usually recommended when fibroids:
- Distort the uterine cavity
- Are linked to infertility
- Cause repeated miscarriages
- Lead to severe pain or bleeding
Small fibroids that do not affect the uterine cavity are often monitored.
Emotional Impact of Fibroids and Delayed Pregnancy
Living with fibroids and infertility can cause:
- Emotional stress
- Anxiety and frustration
- Fear of treatment outcomes
Emotional support and counseling can be very helpful during this journey.
Final Thoughts
Fibroids are common and, in many cases, do not prevent a woman from getting pregnant. However, certain types of fibroids—especially those that affect the uterine cavity—can interfere with implantation or delay conception. Understanding whether fibroids can cause infertility or Delay Pregnancy depends on factors such as the size, type, and location of the fibroids, as well as a woman’s overall reproductive health. With proper evaluation, it becomes easier to identify whether fibroids are playing a role in fertility challenges.
The good news is that effective treatment options are available, and many women with fibroids go on to have successful pregnancies. Seeking timely guidance from a trusted Fertility Clinic, such as Fertility Point, can help ensure the right diagnosis and personalized care plan. With the right support and treatment approach, fibroid-related fertility issues can often be managed successfully, allowing couples to move forward with confidence on their journey to parenthood.
FAQ's
Can fibroids completely prevent pregnancy?
No. Most fibroids do not completely prevent pregnancy. Only certain types may interfere with conception.
Can fibroids cause infertility even with regular periods?
Yes. Regular periods do not rule out implantation-related fertility issues.
Do fibroids always need surgery before pregnancy?
No. Only fibroids affecting fertility or causing symptoms usually require treatment.
How long after fibroid removal can I try to conceive?
Doctors usually recommend waiting a few months for proper healing.
