IVF vs. ICSI: Which is Better?
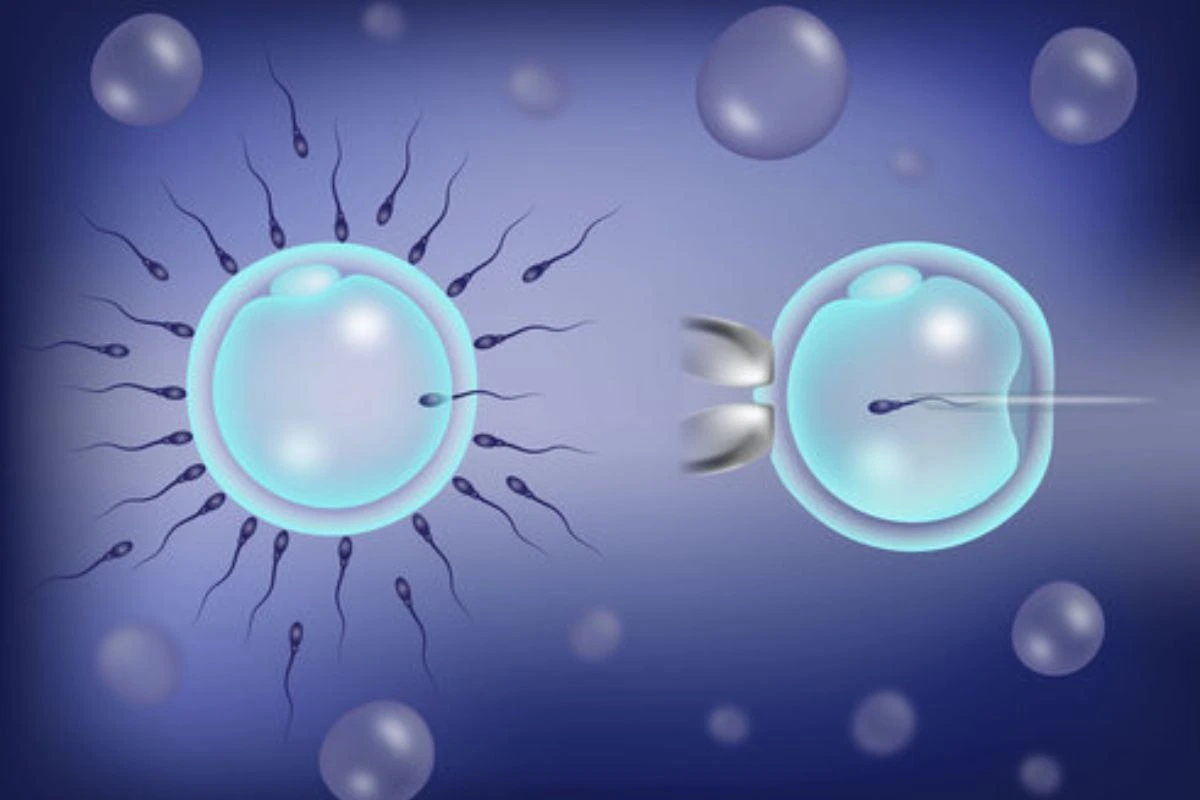
In vitro fertilization (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) are two of the most widely used assisted reproductive technologies. While IVF has been the cornerstone of fertility treatments for decades, ICSI has emerged as a critical technique, especially for overcoming severe male infertility. In Kenya, where access to advanced reproductive technologies is improving, many couples are exploring their options, including ICSI treatment in Kenya. This article will delve into the differences between IVF and ICSI, helping couples understand which method might be better suited to their specific circumstances.
Understanding IVF
IVF involves stimulating the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, which are then retrieved and fertilized in a laboratory setting using sperm. The sperm and egg are combined in a petri dish, and fertilization occurs naturally within this controlled environment. The resulting embryos are monitored for growth and development before one or more are selected for transfer into the uterus.
Understanding ICSI
ICSI is a specialized form of IVF that was developed to help overcome male infertility issues. Unlike traditional IVF, where the sperm naturally fertilizes the egg in a dish, ICSI involves the direct injection of a single sperm into each egg using a fine needle. This technique is particularly useful when there are issues with the sperm's ability to penetrate the egg naturally due to low sperm count, poor mobility, or abnormal morphology.
Comparing IVF and ICSI
-
Indications for Use
-
IVF: Best suited for individuals or couples with unexplained infertility, female tubal blockages, mild male infertility, or those using donor eggs or sperm.
-
ICSI: Specifically designed for cases of severe male infertility, including very low sperm count, poor sperm motility, or sperm that otherwise cannot fertilize an egg naturally. It is also used when previous IVF cycles have failed to result in fertilization.
-
-
Success Rates
-
Both IVF and ICSI offer varying success rates that depend heavily on individual factors like age, fertility health, and the underlying cause of infertility. Generally, ICSI does not increase the chance of pregnancy over IVF unless there are significant male fertility issues.
-
-
Risks and Considerations
-
IVF: The main risks include ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), multiple pregnancies, and stress. There's also a risk of non-fertilization, but this is less common.
-
ICSI: Since ICSI involves more manipulation of both sperm and egg, there's a slightly higher risk of damage to the eggs and potential genetic issues in embryos. However, modern techniques and experienced practitioners minimize these risks.
-
-
Cost and Accessibility
-
Typically, ICSI is more expensive than standard IVF due to the additional equipment and expertise required to perform the procedure. In Kenya, while both IVF and ICSI treatment are available, ICSI might be less accessible and more costly.
-
-
Personal Factors
-
The choice between IVF and ICSI often depends on personal factors such as the couple’s medical history, the specific nature of their infertility, and previous experiences with assisted reproductive technologies.
-
Conclusion: IVF or ICSI?
Deciding whether IVF or ICSI is better depends largely on the specific infertility issues being addressed. For couples where male infertility is not a concern, IVF remains a strong and effective option. However, for couples struggling with severe male infertility, ICSI offers a more targeted and often more effective solution.
For those exploring these options, consulting with fertility specialists who offer ICSI treatment in Kenya is crucial. These specialists can provide detailed assessments and recommend the best treatment path based on thorough diagnostic testing and the couple’s overall reproductive health and preferences. This personalized approach ensures that couples receive the most appropriate and effective treatment to maximize their chances of a successful pregnancy.
FAQ's
What is the difference between IVF and ICSI?
In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF) mixes eggs and sperm in a lab dish for natural fertilisation. Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) injects a single selected sperm directly into the egg to ensure fertilisation.
Who should consider ICSI instead of standard IVF?
ICSI is especially recommended when male-factor infertility exists—such as very low sperm count, poor motility or abnormal shape—or when previous IVF cycles failed to fertilise eggs.
Is one procedure clearly better than the other?
Not universally. IVF and ICSI can both be effective, but the right choice depends on your specific infertility factors. ICSI offers more control for sperm issues, while IVF is often suitable for broader infertility scenarios.
Do success rates differ significantly between IVF and ICSI?
Both treatments offer good outcomes when properly matched to a couple’s situation. ICSI may boost fertilisation in male infertility cases, but it doesn’t automatically guarantee higher overall pregnancy or live-birth rates in other situations.
